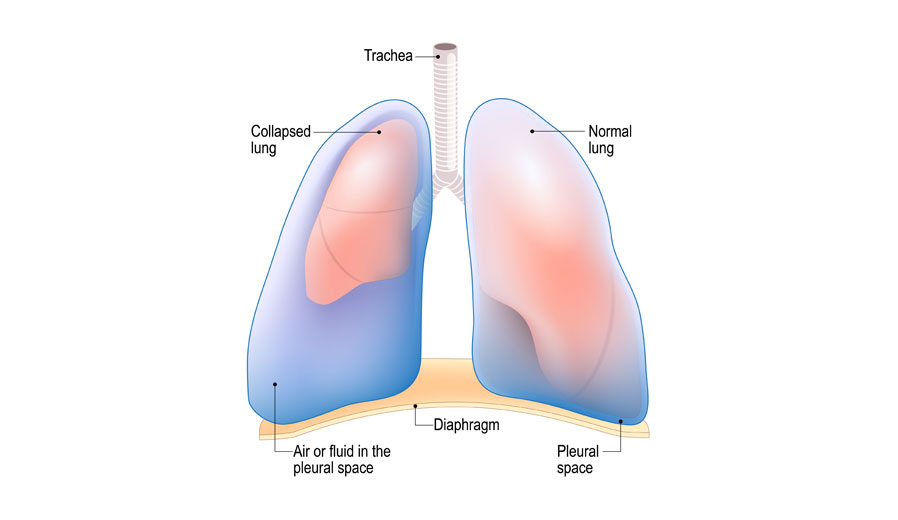
The pleural is the film that lines the thoracic (chest) cavity and covers the lungs. It resembles a huge sheet of tissue that folds over the outside of the lungs and lines within the chest pit. The chest (thoracic or pleural) cavity is a space that is encased by the spine, ribs, and sternum (bosom bone) and is isolated from the midsection by the stomach.
Types of Pleural Diseases
- Hemothorax: Accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity.
- Pleural effusion: Accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural cavity; this accumulation pushes against the lung and prevents full expansion with breathing.
- Empyema: The accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity. This is a type of pleural effusion that is usually associated with pneumonia (an infection in the adjacent lung).
- Pleural tumors: Dangerous cancers emerging from the pleura (for example mesothelioma) or spreading to the pleura (metastatic) from another site, and harmless cancers emerging from the pleura
- Pneumothorax: Collection of air inside the pleural pit between the outside of the lung and within the rib confine.